Laser cutters are versatile solutions to a variety of industrial and commercial challenges. With the right laser cutting machine, industrial and commercial organizations can meet their needs for engraving, cutting or marking a wide range of different materials, and their technology stands out from the competition.
1. Laser Cutting Use
Laser cutters are universal in the sense that they can perform different operations depending on how the user or operator configures their settings. Laser cutting, engraving, marking, and even laser etching can all be performed by the same machine under different operating conditions, and each function is suitable for a different type of application.
Laser cutting is the use of a laser engraver to cut an entire shape or section from a selected material. High-power laser machines are the best choice for cutting plastic and metal substances because they interact directly with the material, not just the pigments in the material. Some metals have high enough melting points to be laser-cut, but nearly all fabrics and paper-based materials can be easily shaped by laser cutting.
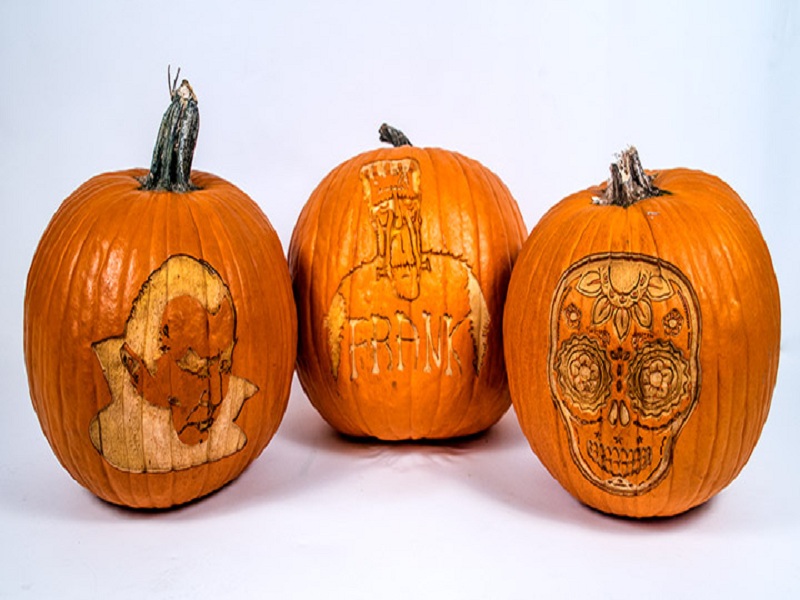
Laser engraving uses a high-power laser to burn the surface of the material, leaving visible marks between 0.02" and 0.125" deep. Laser engraving is a useful process for personalizing or customizing objects made of wood, leather, acrylic, glass, or stainless steel.
Laser engraving is a special type of engraving technique that allows extremely shallow cuts, typically only 0.001 inches deep.
Laser marking is often used to create permanent barcodes or other traceability marks on metal products, such as medical devices or automotive or aerospace parts. Laser marking does not cause any physical changes to the material as it is done using only a low-power laser. The beam causes oxidation under the metal surface, discoloring it and leaving a permanent, high-contrast mark. Laser marking is effective on flat, curved, and round surfaces.
2. Vector Cutting Machine is Accurate and Reliable
Both mechanical and laser cutting are common manufacturing processes across the manufacturing industry today, but there is a reason why more and more manufacturers are choosing to rely on laser cutting machines for their needs.
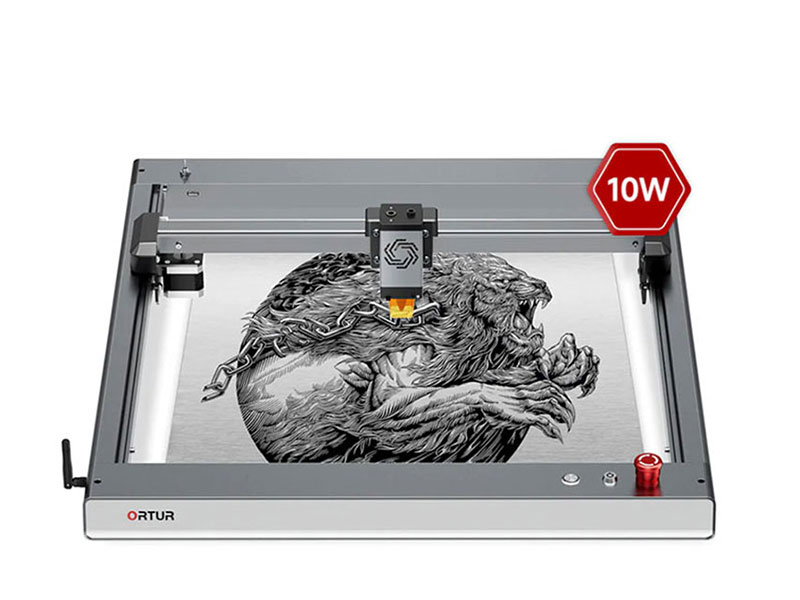
The reason is the unmatched precision and reliability of CNC vector cutters, which provide absolute consistency and help minimize risk throughout the cutting process. On the laser cutting machine, Ortur Laser Master 3 is recommended for laser cutting. Compared to mechanical cutting, laser cutting offers:
The ability to surface finish products while machined parts may require post-processing to finish them
There is no direct contact between the material and the laser cutter, reducing the possibility of material contamination or an accidental marking
Less heat is generated in a smaller area than mechanical cutting, reducing the risk of material warping or warping at the cut site
The laser engraving process is also superior to its industrial counterpart computer rotary engraving. Using a laser, the time and labor required to set up an engraving job is reduced, and laser engraving can be used to mark a wider range of metals and other materials.
Some manufacturers continue to use chemical etching to mark their products, but laser marking is certainly a more efficient option. The LaserPeker 2 laser marker, for example, can produce consistent marks with 99.9% accuracy on a variety of materials, even in different shapes. Processes such as chemical etching, the success of which depends on the variable absorption rate of the chosen acid material, often produce marks with up to 50% error/defect rate. Chemical etching lacks the precision and reliability of laser etching when it comes to producing high-quality, long-lasting laser marks.
3. Laser Cutting for a Variety of Materials
Have you ever wondered "what can you cut with a laser cutter?" The answer is, pretty much anything. Laser cutting works by directing a highly concentrated laser beam onto the desired surface through a series of lenses that amplify its intensity. When the laser beam hits the material on the target surface, it is either vaporized, melted, burned away, or blown away by the gas jet.
Lasers are used to cut, etch, mark and engrave materials for a variety of applications. On the industrial side, auto and aerospace parts manufacturers use laser cutters to mark parts with unique traceability numbers, or product identification numbers, that allow regulators to trace each part's path through the supply chain. Product designers use laser cutting to create home decor products and other crafts. The versatile applications of laser cutters are due in part to the versatility of laser cutting materials, including:
- Acrylic
- Mylar film is also known as polyester
- Nylon
- Two-color acrylic
- Polyethylene and Polypropylene
- Stainless steel
- Anodized aluminum
- Fabrics such as suede, leather, linen, and cotton
- Sheet metal, including magnets
- Document
- Rubber products such as neoprene and fluororubber
- Wood
Aerospace parts manufacturers benefit from the versatility of laser engravers and cutters as they can be used to mark electrical wires made of rubber, custom dashboards made of two-tone acrylic, and mechanical parts made of stainless steel.
4. Laser Engraving and Cutting are Very Safe
Laser cutters are becoming more common on job sites, public workshops and "maker spaces" and even in schools - but what are the risks?
The lasers in a typical laser engraver will be marked as Class 3B or Class 4 - high power laser beams capable of causing serious skin or eye damage.
Nonetheless, laser cutters are designated as "low risk" under the standard because they are fully enclosed and interlocked. Users should not manipulate safety features or intentionally expose their skin or eyes to the laser beam - otherwise, laser engraver are extremely safe and low risk.
Conversely, alternatives to laser cutting can pose a significant threat to worker safety. The chemicals used in acid etching are toxic if ingested and can corrode the skin, making the mechanical manufacturing process more likely to injure workers than laser cutters.
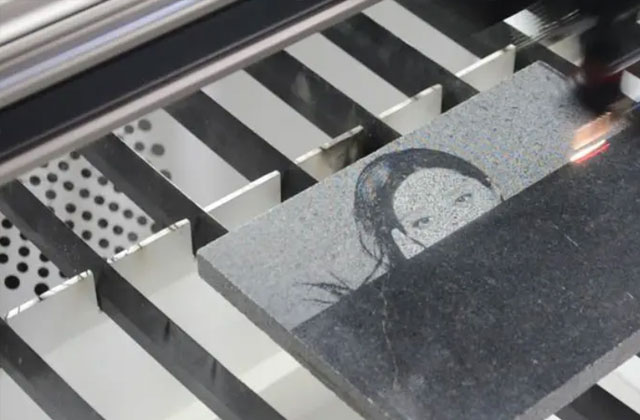
Description: In desktop laser markers such as these, the laser is housed in an enclosure that should always be closed when a program is active. As a result, machine operators are never exposed to laser beams strong enough to seriously damage eyes or skin. Its compact design and inherent safety make benchtop laser cutters popular for marking small medical implants or industrial parts.
5. Laser Cutters Produce Very Little Waste
One of the best things about operating laser cutters in your workshop or production line is that they do not generate any real waste and do not require any consumables.
In contrast, the only consumable used by a laser cutter is electricity, so you don't need a new waste removal process or order additional products.
Laser-cutting and engraving machines offer significant benefits to the organizations that use them. These versatile machines can perform a variety of applications including engraving, cutting, or marking various materials (stainless steel, plastic, wood, paper, etc.). In addition to precision and reliability, laser cutters are valued for their excellent safety and the fact that they do not waste material. And more and more people like to use laser engraving machines.
If you need any laser engraving machine, you can go to HTPOW online store to buy and consult, we will help your laser engraving business with the most professional and excellent service.